The Transformative Benefits of Agentic BI
Traditional BI is reactive by nature - it waits for someone to ask a question, run a query, or notice an anomaly in a dashboard. AI agents fundamentally change this dynamic by proactively monitoring data, identifying patterns, and taking action without waiting for human intervention.
This shift from reactive to proactive intelligence delivers five key benefits that are reshaping how organizations leverage their data:
Proactive Insights
Agents identify problems and opportunities without waiting for queries. They detect anomalies, forecast patterns, and alert the right people at the right moment.
Improved Decision Quality
Analyze multiple sources and scenarios to recommend the most data-backed course of action, reducing uncertainty in strategic decisions.
Time & Resource Savings
Automate repetitive tasks like report generation. A documented case achieved savings of "hundreds of hours of manual processes."
Operational Scalability
Monitor thousands of metrics simultaneously without adding operational overhead - something unsustainable with manual management.
True Data Democratization
Natural language interfaces eliminate the need to know SQL. Any user can ask questions and get clear answers.
The Hallucination Problem: AI's Achilles Heel
For all their transformative potential, AI agents face a critical challenge when working with enterprise data: hallucination. Large Language Models (LLMs) can generate confident, plausible-sounding responses that are factually incorrect - a catastrophic problem when the output drives business decisions.
Without proper grounding, an AI agent might confidently report "Q3 revenue increased 15%" when the actual figure was 5% - or worse, reference metrics that don't exist. In regulated industries like finance or healthcare, such errors can result in compliance violations, financial losses, and reputational damage.
The root cause is simple: LLMs are trained on general knowledge, not your specific data model. They don't inherently understand what "revenue" means in your organization, which tables contain it, how it should be calculated, or what business rules apply.
This is where the semantic layer becomes the critical trust anchor.
The Semantic Layer: Grounding AI in Truth
The semantic layer provides a governed, centralized definition of business concepts. It acts as a translation layer between raw data and business understanding - and it's exactly what AI agents need to generate accurate, trustworthy outputs.
"The semantic layer transforms AI agents from general-purpose chatbots into specialized business analysts who speak your company's language and respect your data governance policies."
The Trust Anchor: The Semantic Layer as a Barrier Against Misinformation
For agents to act reliably, their decisions must be grounded in a single source of truth. Looker's semantic modeling layer (LookML) acts as this indispensable trust anchor.
How Grounding Works with LookML
- Verified Business Logic: Metric definitions and "business truths" reside in LookML, not in the LLM.
- Governed Query Generation: When an agent receives a natural language question, it uses LookML to build a precise, governed query.
- Guaranteed Consistency: The agent's response is identical to what you'd see in a Looker dashboard, ensuring total analytical consistency.
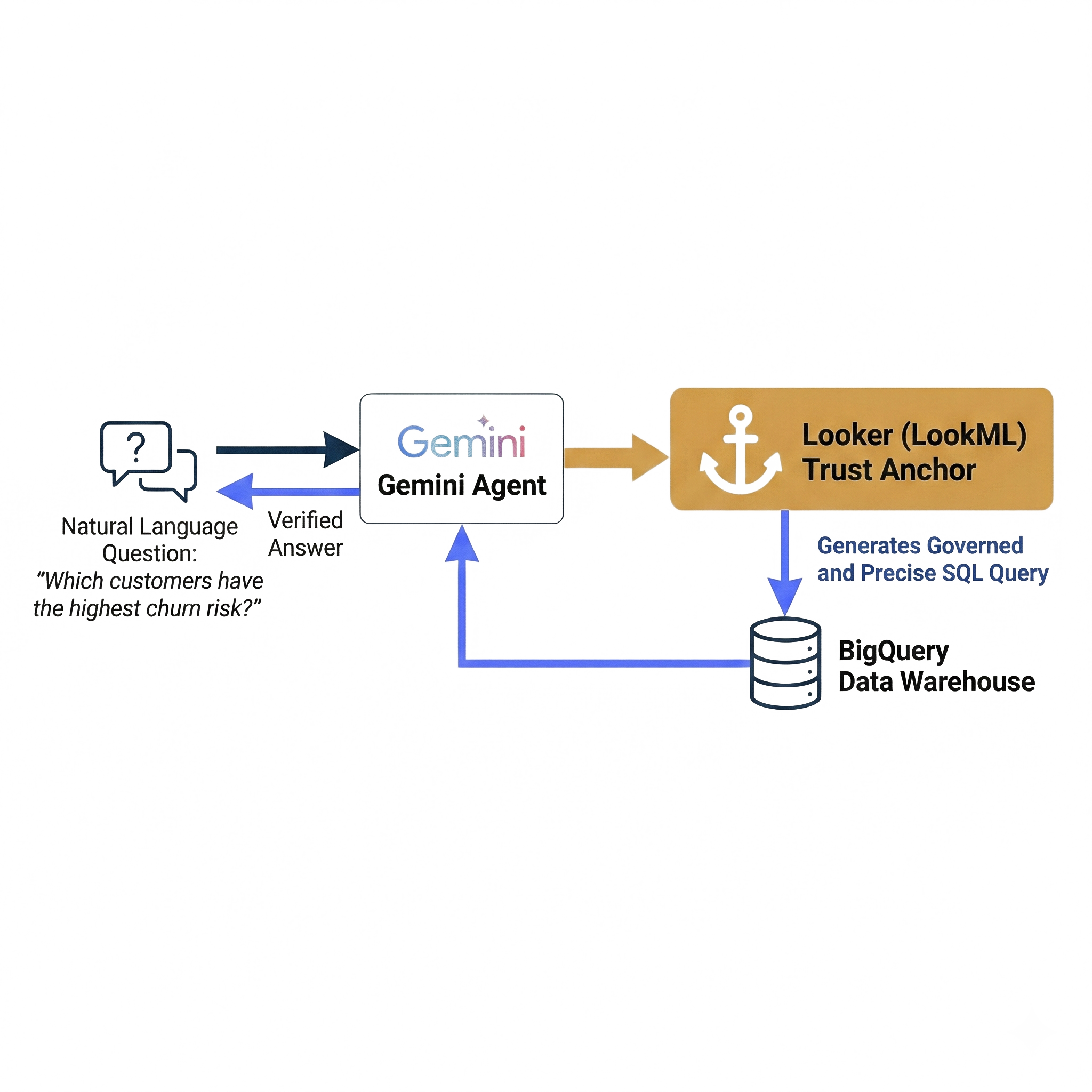
Result
LookML becomes the technical barrier against algorithmic misinformation, transforming BI from a visualization tool into a critical component of AI governance and verification.
LookML: The Grounding Language
LookML defines every business concept an agent can reference. When a user asks about "revenue," the agent knows exactly:
- Which table contains the data (orders, transactions, etc.)
- Which calculation to apply (SUM, filtered aggregations, etc.)
- What dimensions are valid for grouping (region, product, time)
- What access rules apply (row-level security, data masking)
# This is what the AI agent "sees" when asked about revenue
view: orders {
sql_table_name: analytics.fct_orders ;;
# Dimension: When did this order occur?
dimension_group: order {
type: time
timeframes: [date, week, month, quarter, year]
sql: ${TABLE}.order_timestamp ;;
}
# Dimension: Geographic segmentation
dimension: region {
type: string
sql: ${TABLE}.region_code ;;
description: "Sales region (AMER, EMEA, APAC)"
}
# Measure: Total Revenue - THE GOVERNED DEFINITION
measure: total_revenue {
type: sum
sql: ${TABLE}.order_total ;;
value_format_name: usd
description: "Total order value in USD, excluding returns"
# Agent knows this excludes cancelled orders
filters: [order_status: "-cancelled, -returned"]
}
# Measure: Q3 Revenue - Pre-defined for common queries
measure: q3_revenue {
type: sum
sql: ${TABLE}.order_total ;;
value_format_name: usd
filters: [
order_quarter_of_year: "Q3",
order_status: "-cancelled, -returned"
]
}
}With this grounding, when a user asks "What was Q3 revenue by region?", the agent doesn't guess - it generates a precise query using the governed definitions:
-- Agent-generated query grounded in LookML
SELECT
orders.region_code AS region,
SUM(CASE
WHEN EXTRACT(QUARTER FROM orders.order_timestamp) = 3
AND orders.order_status NOT IN ('cancelled', 'returned')
THEN orders.order_total
ELSE 0
END) AS q3_revenue
FROM analytics.fct_orders AS orders
WHERE EXTRACT(YEAR FROM orders.order_timestamp) = 2025
GROUP BY 1
ORDER BY q3_revenue DESC;Reference Architecture for Enterprise Agentic AI
A robust and scalable agentic AI solution requires a modern, integrated data stack that supports everything from real-time ingestion to autonomous, governed action.
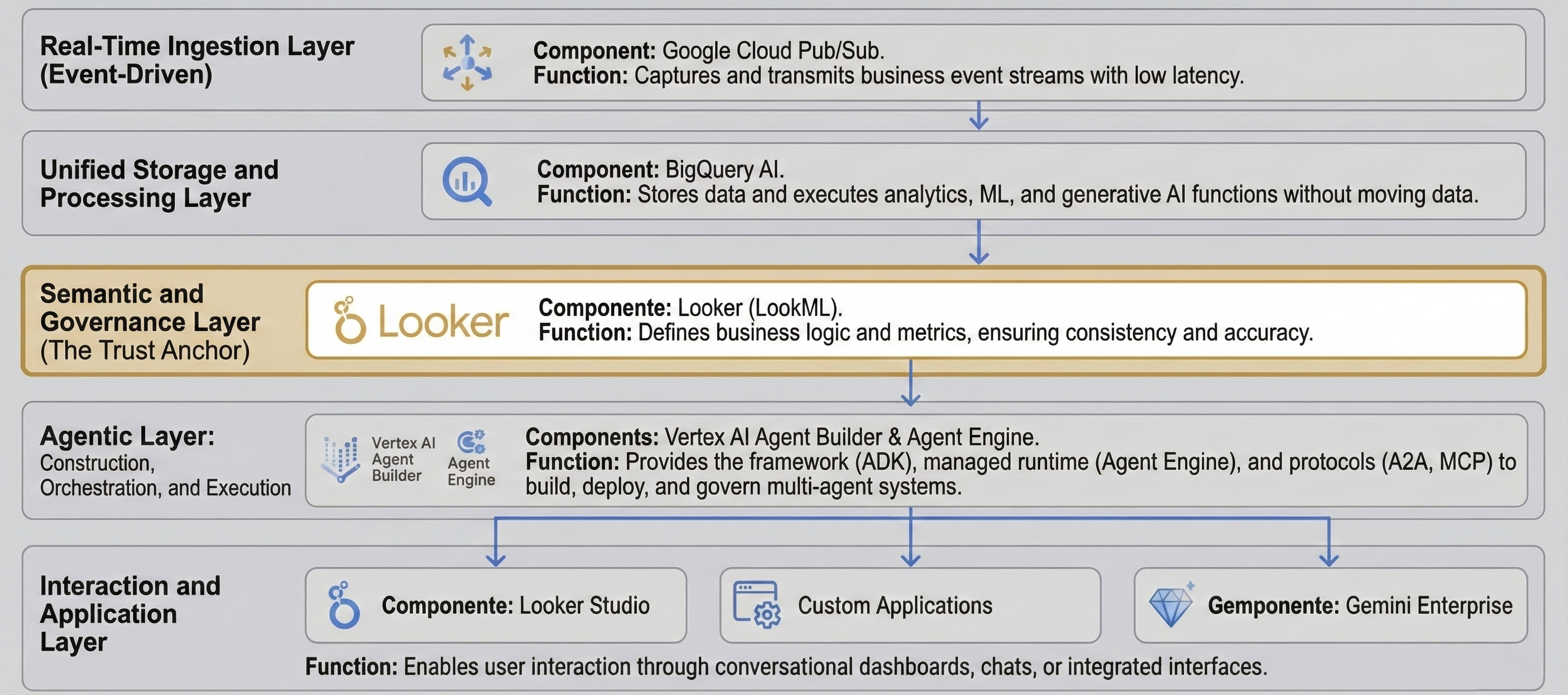
From Idea to Production: Build, Scale & Govern Agents
Vertex AI Agent Builder provides a comprehensive, open platform to manage the complete agent lifecycle, bridging the gap between prototype and enterprise-scale production.
- Tool: Agent Development Kit (ADK) in Python, Go, Java
- Capability: Flexible framework to define agent logic, context management, and tool usage. Deploy with a single command (
adk deploy).
- Platform: Vertex AI Agent Engine (AE)
- Capability: Managed, secure runtime providing observability (metrics, traces), persistent memory management, and user simulator for evaluation.
- Capability: Native agent identities (IAM Principals) for least-privilege access control.
- Integration with Security Command Center for threat detection.
AI Agents vs Traditional Assistants: The Key Differences
Understanding the distinction between AI agents and traditional AI assistants is crucial for proper implementation and expectation-setting:
| Capability | Traditional AI Assistant | AI Agent (Agentic AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Waits for explicit instructions | Proactively monitors and acts on triggers |
| Context | Single-turn or limited memory | Persistent context across sessions |
| Actions | Generates text responses | Executes workflows, APIs, notifications |
| Integration | Standalone chatbot | Connected to ERP, CRM, BI, and external systems |
| Governance | Manual review of outputs | Built-in audit trails, access controls, guardrails |
| Learning | Static model knowledge | Continuous adaptation to new data patterns |
The Indispensable Component: Human Oversight
Agent autonomy does not eliminate human responsibility - it redefines it. Human oversight is a non-optional pillar of the system, essential for ethics, accountability, and trust.
Why Human Oversight is Critical
- Bias Mitigation & Ethics: Necessary to establish ethical guidelines and review decisions in complex contexts where algorithms could perpetuate biases.
- Legal Accountability & Auditing: Ensures traceability and accountability, a key requirement of regulations like the EU AI Act.
- Exception Handling (Human-in-the-Loop): The system must escalate ambiguous or high-risk cases to human reviewers for final validation.
- Trust Building: Trust is built knowing there's human control ensuring AI operates safely and aligned with company values.

Navigating the Path: Key Implementation Challenges
Adopting agentic AI is not without obstacles. Organizations must prepare to face five fundamental challenges that will determine the success of their implementation:
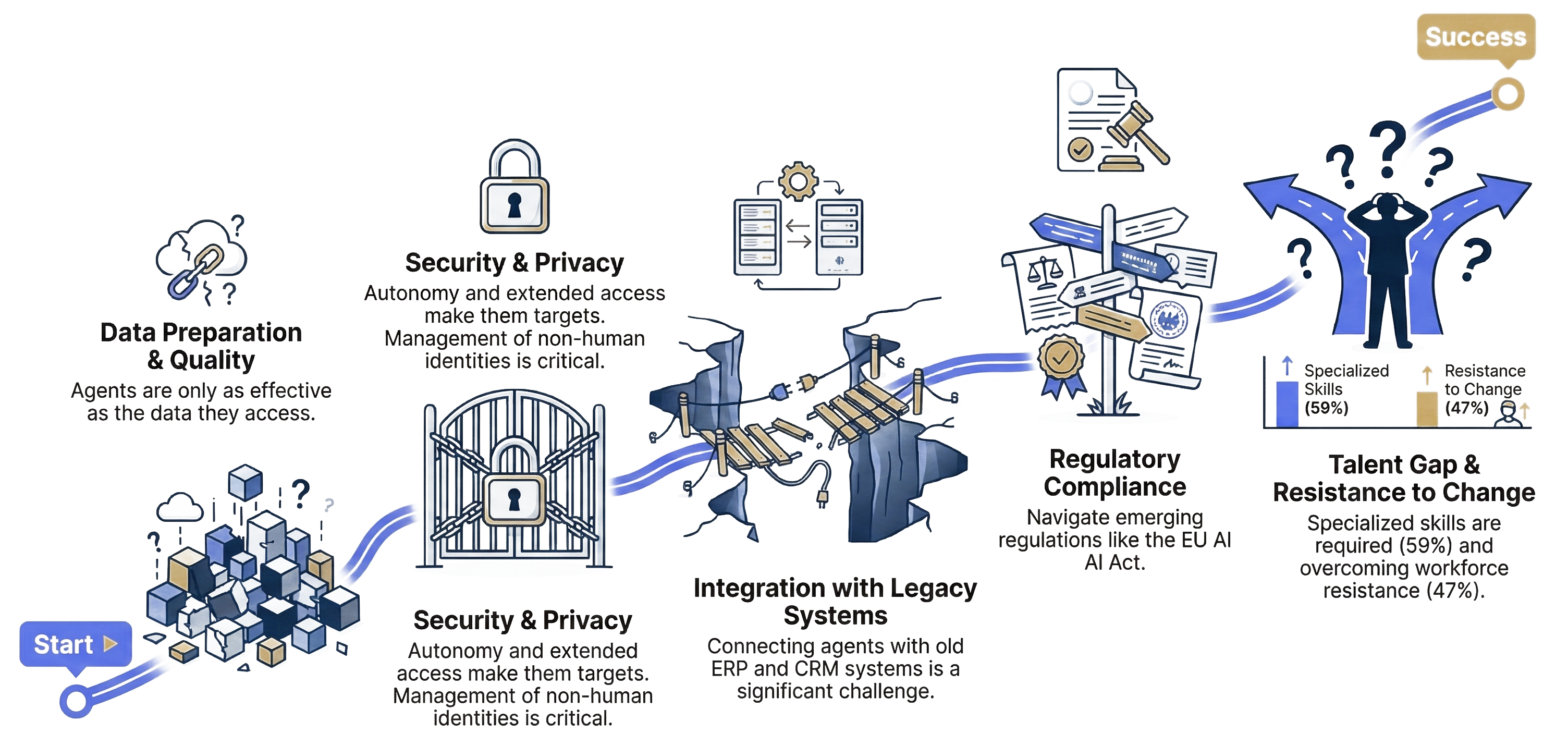
The New Horizon: From Asking Data to Conversing with Action
Agentic AI doesn't replace business intelligence, it expands it. It transforms BI from a passive observation discipline into an enterprise nervous system capable of perceiving, deciding, and acting in real time.
The Future of BI is Agentic
Conversational: Users dialogue with their data in natural language, without technical barriers.
Proactive: Systems anticipate needs and alert about opportunities and risks before they materialize.
Action-Oriented: From passive insights to decisions automatically executed within defined guardrails.
"The true paradigm shift is conceptual: we move from asking data to conversing with systems that understand context, remember history, and can act on our behalf."
In the next section, we'll explore real-world use cases across industries - from retail demand sensing to healthcare resource optimization - showing how leading organizations are implementing agentic BI today.