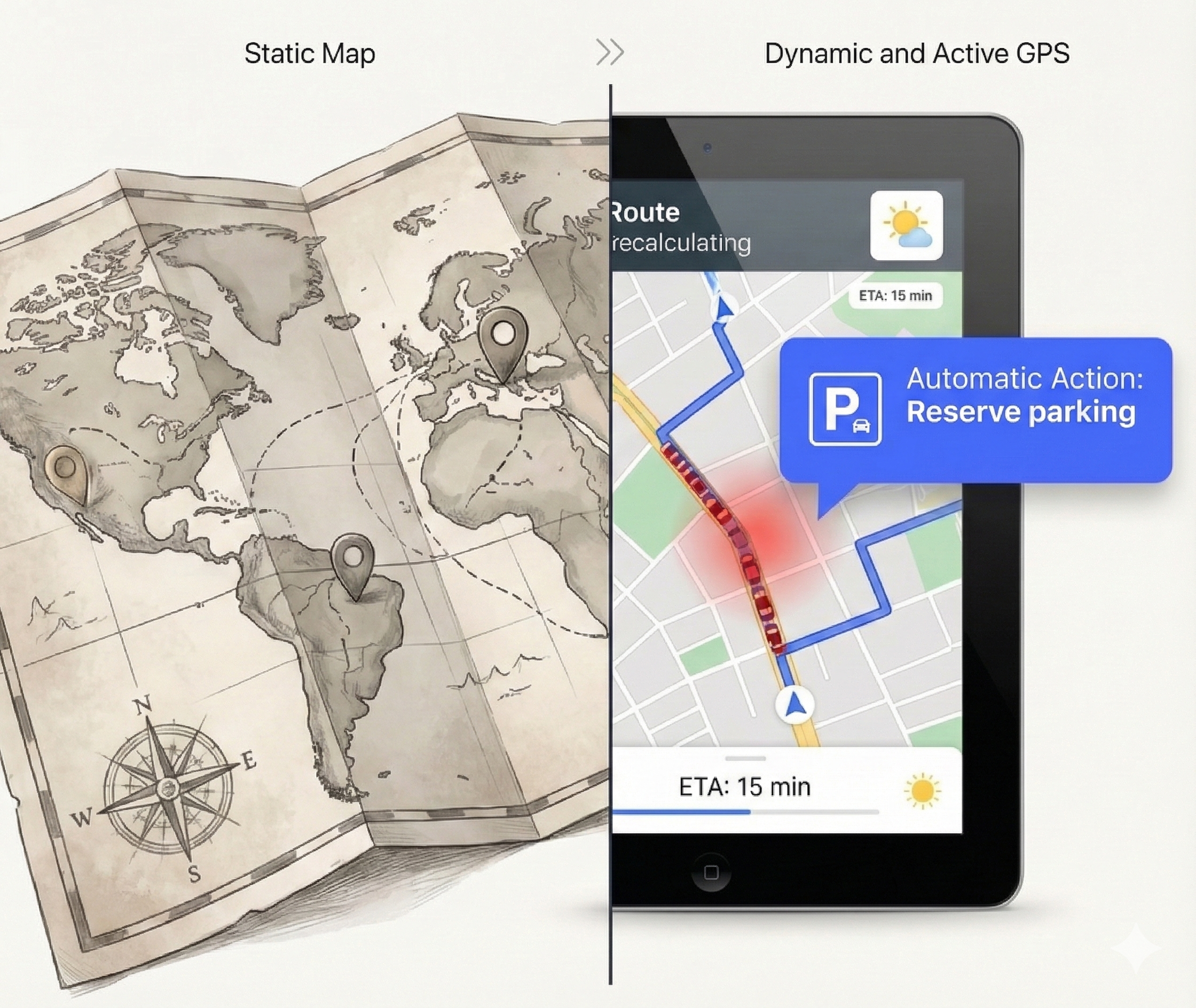
Traditional Business Intelligence has been fundamental for understanding performance. It provides us with a detailed map that answers two critical questions: What happened? and What is happening now?
BI platforms centralize data from sales, finance, and marketing, making it accessible through dashboards, reports, and KPIs. They are essential for establishing a shared vision of performance. Data integration, ETL processes, centralized dashboards, KPI tracking, real-time alerts, and drill-down visualizations - these are the core components that have served organizations for decades.
"Traditional BI tells you what's happening, but rarely tells you what to do next."
The Critical Gap: From Insight to Execution
The main challenge of traditional BI is not the lack of data, but the time and manual effort required to convert an insight into concrete action. This cycle is inherently reactive and costly.
Each step introduces delays and manual effort. By the time an organization acts on an insight, the window of opportunity may have already closed. This reactive cycle is not just slow - it's increasingly unsustainable in a world that demands real-time responses.
The Evolution Toward Autonomy: The AI Agent
An AI Agent is a software entity designed to perceive its environment, reason about objectives, and take actions autonomously. They don't just display information - they actively support decision-making and execution, functioning as digital team members.
The AI Evolutionary Leap (OpenAI Framework)
- Level 1: Conversational Assistants - Respond to basic instructions
- Level 2: Reasoning Assistants - Solve structured tasks
- Level 3: Autonomous Agents - Plan, execute actions, and adapt. We are here now.
- Level 4: Collaborative Agents - Cooperate with each other
- Level 5: Integral Organizational Systems - Replicate team operations
The Qualitative Leap: From Passive Assistants to Proactive Agents
The change is not incremental - it's transformational. AI agents introduce a new level of autonomy, integration, and governance into workflows.
| Aspect | Traditional AI Assistants | AI Agents (Agentic AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction | Reactive: Responds to specific queries | Proactive: Continuous dialogue, plans and adjusts on the fly |
| Autonomy | Passive: Needs direct, explicit instructions | Proactive: Initiates tasks, monitors events, acts on business rules |
| Integration | Isolated: Generally in POCs or embedded chatbots | End-to-end: Native connection with ERP, CRM, BI, external APIs |
| Governance | Manual: Sporadic review of interactions | Automated: Immutable traceability, audits, real-time alerts |
The Adoption Is Already Underway and Accelerating
The transition to agentic AI is not theoretical. Organizations are investing and rapidly moving beyond experimentation phases to implement concrete solutions.
Key Market Statistics (2025)
of organizations already use AI in some business task
(Matteria)have moved beyond the AI experimentation phase
(KPMG)"The real paradigm shift is conceptual. Companies will stop asking questions to data and start conversing with it. In that conversation, agents will be the new interlocutors of knowledge and action."
In the following sections of this edition, we'll dive deep into the benefits of agentic BI, real-world use cases across industries, the critical role of the semantic layer as a trust anchor, and the complete reference architecture for implementing enterprise-grade AI agents.
The future of BI is not just about visualizing data - it's about AI agents that understand, decide, and act.
- Martin Velez
Founder, RavencoreX